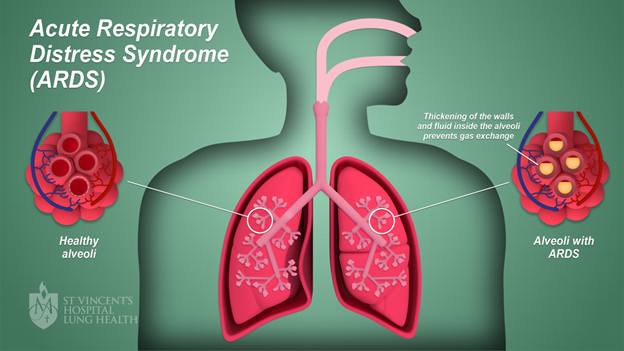
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a serious condition affecting the lungs. It's a type of acute respiratory failure where the lungs can't provide enough oxygen to the body. The ARDS definition medical community provides highlights the condition involves rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. When trying to define ARDS, it is critical to note it can occur in anyone, including infants, adults, and ARDS in pediatrics. Increasing public understanding of ARDS disease and its impact is essential for prevention and early diagnosis.
Raising awareness about ARDS symptoms and treatment can help save lives. ARDS meaning involves compromised oxygen levels due to fluid-filled air sacs in the lungs. Early recognition and prompt intervention significantly improve outcomes for individuals. ARDS remains challenging because its symptoms overlap with other pulmonary conditions like pneumonia and very early signs of ARDS, such as mild difficulty breathing, can be easily overlooked.
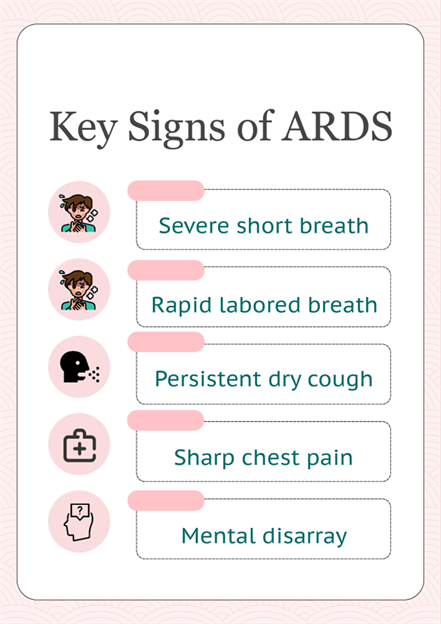
Recognizing the Symptoms and Risks of ARDS
Recognizing ARDS signs early is crucial. Typical clinical manifestations of ARDS include: 1. Severe shortness of breath 2. Rapid, labored breathing 3. Persistent cough 4. Chest pain 5. Confusion or disorientation
High-risk groups include individuals suffering from septic shock and ARDS, pneumonia, or major injuries. It can also affect individuals with other underlying health conditions, including ARDS and COPD, and disturb those suffering from ARDS pneumonia. Those with recent infections or trauma face increased risks. Certain medical interventions like mechanical ventilation can further increase the probability of ARDS in ICU settings. Awareness about these most common causes of ARDS is necessary for timely medical consultation.
Uncovering the Causes and Development of ARDS
The ARDS etiology involves multiple factors. Sepsis and pneumonia are among the most common causes of ARDS. COVID-19 ARDS, which characteristically complicates respiratory symptoms, also contributes to ARDS due to COVID issues. Factors like inhalation of toxic substances or aspiration of vomit complicate ARDS causes further. ARDS icd 10 recognizes it as a complication often hidden in patients dealing with other critical conditions.
Without prompt ARDS treatment, the syndrome progresses swiftly. Fluid leaks from the smallest blood vessels in the lungs into air sacs, making breathing difficult. Diagnosing ARDS becomes imperative as untreated, it can result in lasting lung damage or death. Understanding this progression underscores the critical nature of ARDS radiology.
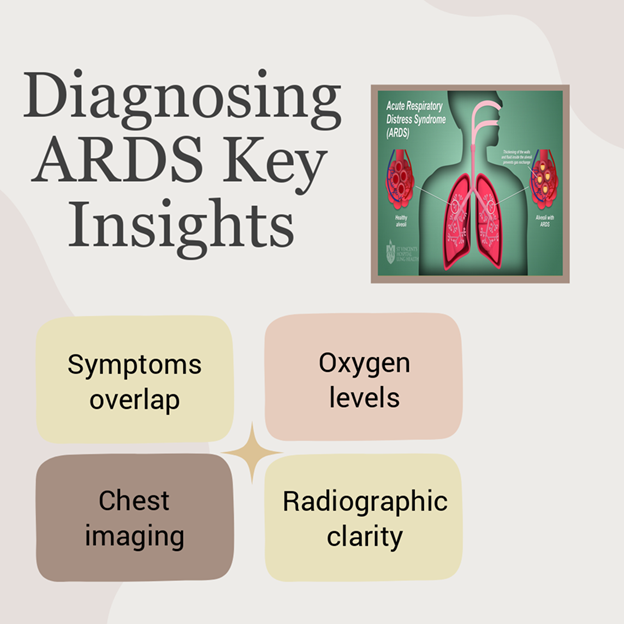
Diagnosis and Treatment: Navigating ARDS Care
Diagnosing ARDS accurately can be challenging due to symptom overlap with other conditions. Medical professionals rely on two primary diagnostic measures: - Oxygen levels and chest imaging to confirm ARDS radiopaedia. - ARDS in lungs clearly captured through chest X-rays or CT scans.
Effective ARDS treatment requires a comprehensive plan. ARDS medicine often includes: - Oxygen therapy to maintain adequate oxygen levels. - Mechanical ventilation for advanced support, ensuring the patient's breathing remains stable.
Innovations in care have emerged, including prone positioning, where patients lay on their stomachs to improve oxygen flow. Respiratory distress syndrome blood pressure support addresses hemodynamic issues. Nutritional support fosters overall recovery.
In cases involving ARDS on ventilator care, minimizing the duration of mechanical assistance is crucial for recovery. Additional treatments focus on minimizing infections and complications. Professionals may employ medications like steroids to reduce lung inflammation.
Advanced technologies like ARDS net and ARDS osmosis have enhanced treatment protocols. Personalizing care plans per individual characteristics is key. Recognizing differences between types of ARDS, as in the case of moderate ARDS, affects decisions regarding the regimen and therapy approach.
Lifestyle, Recovery, and Ongoing Health Management
Managing lifestyle factors can play a vital role in reducing ARDS risk. Avoiding high pollution areas and quitting smoking minimize the chances of respiratory distress. During recovery, some patients may experience prolonged weakness, requiring continued care and therapy.
Recovery from ARDS medical treatment may necessitate long-term healthcare. Rehabilitation can include physical therapy and mental health support.
Living post-ARDS involves regular check-ups and monitoring. Patients are advised to: - Follow health provider recommendations diligently. - Keep consistent in follow-up visits.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways on ARDS
Understanding the significance of early symptom recognition in ARDS care can't be overstated. Increased awareness and ARDS explained help demystify the condition. Supporting loved ones fighting ARDS in medical terms can empower families and communities. Tapping into community resources strengthens the recovery process, providing the support necessary for long-term health.
Take Control of Your Respiratory Health at Rajnish Hospitals
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) can be a serious condition, but with early detection and expert care, recovery is possible. At Rajnish Hospitals, we offer comprehensive diagnostics and advanced treatments for ARDS, ensuring that you receive the best care possible.
If you're experiencing symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or fatigue, don’t wait. Book your consultation today with our respiratory specialists and take the first step towards better lung health. Your health is our priority!